Search Engine Positioning
What is Search Engine Positioning?
Search engine positioning is the continuous practice of optimizing web pages in order to achieve higher (or more numerous) results in search engines for specific keywords.
In other words:
Search engine positioning is a subset of search engine optimization that focuses on achieving higher rankings for specific pages (as opposed to working on sitewide technical SEO improvements or choosing keywords to optimize for).
Why is Search Engine Positioning Important?
A recent industry study that we conducted here at Backlinko found that the top 3 results get the lion’s share of organic clicks.
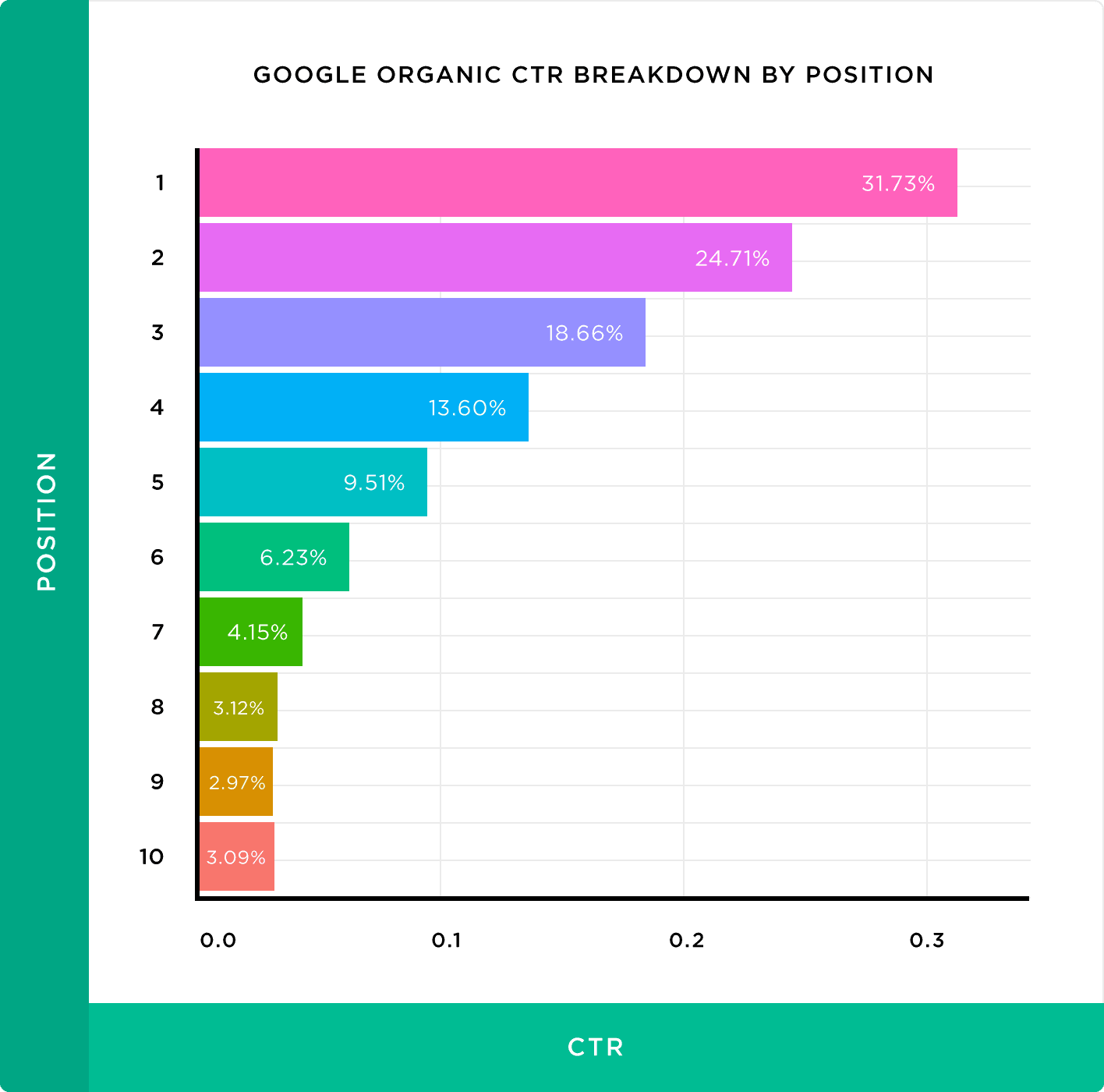
We also discovered that moving up just one spot can improve CTR by 30%.
That said, search engine positioning only about getting higher Google rankings.
That’s because the Google SERPs aren’t just a list of 10 blue links anymore.
Instead, Google’s first page now contain lots of “SERP Features”, including:
- Featured snippets
- “People also ask” boxes
- Knowledge graphs
- Top stories
- Video results
For example, take a look at this SERP:
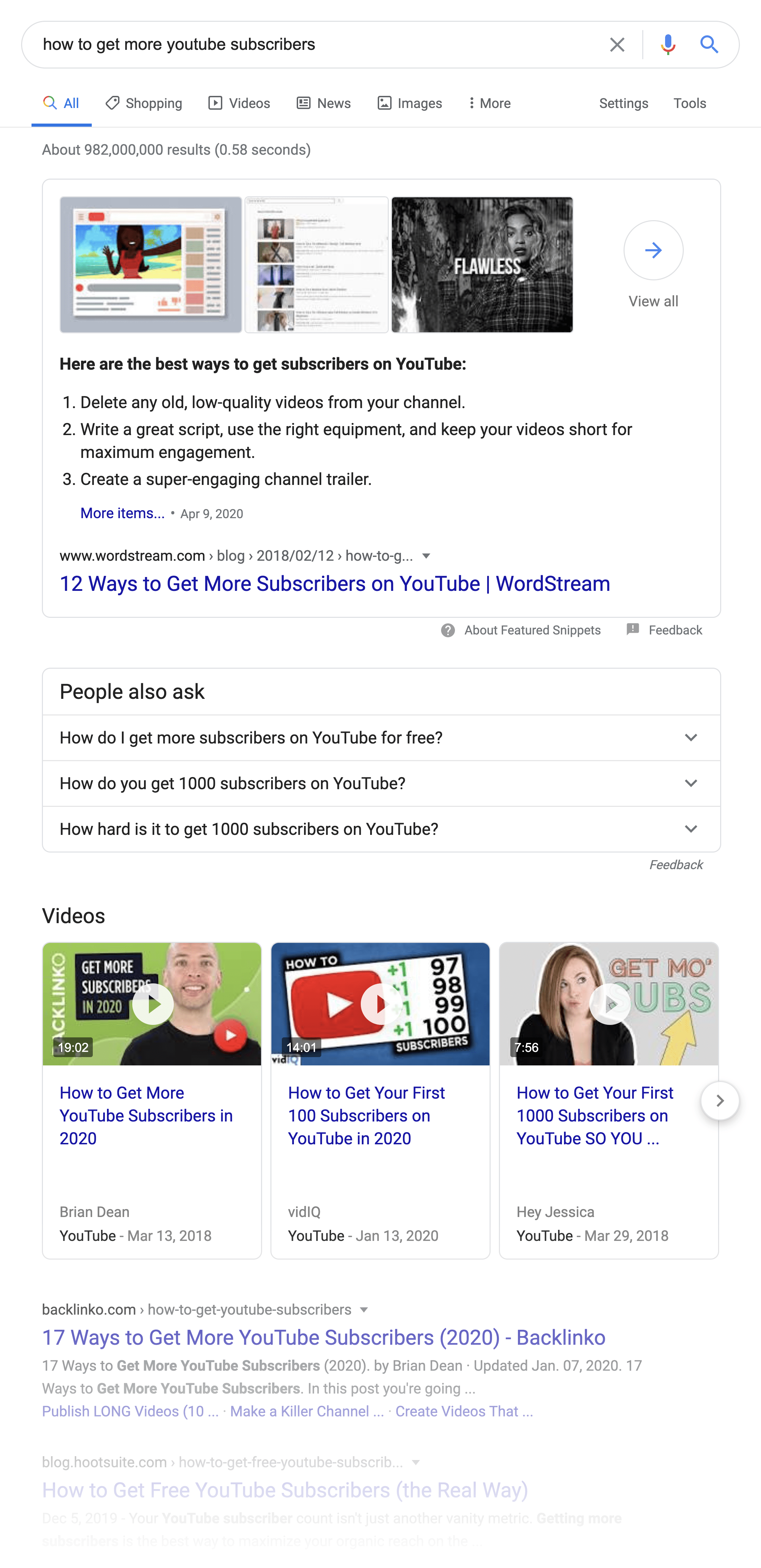
You’ve got a large Featured Snippet box at the top of the page. Video results. And more.
Which means that improving your search engine positioning isn’t just about moving up a few spots.
It’s also about maximizing your “SERP real estate”.
This means ranking as high as you can.
But it can also involve ranking multiple times on the same page.
Or getting rich snippets so that your site stands out from the rest of the pack.
With that, let’s cover exactly how to maximize your search engine positioning in Google.
Step #1: Re-Optimize Your Existing Content
Your first step is to make sure that your current pages are 100% optimized for SEO. Especially pages that are already ranking on the first or second page.
Why is this important?
Well, Google already thinks your site is a relevant result for your target keyword.
(Otherwise you wouldn’t be anywhere near the first page of the search results)
So all you need to do is make some on-page SEO and UX improvements to that page. And you’ll be primed for higher rankings.
The Search Console is the best way to find pages that need a little boost.
First, login and go to your website’s “Performance” section.
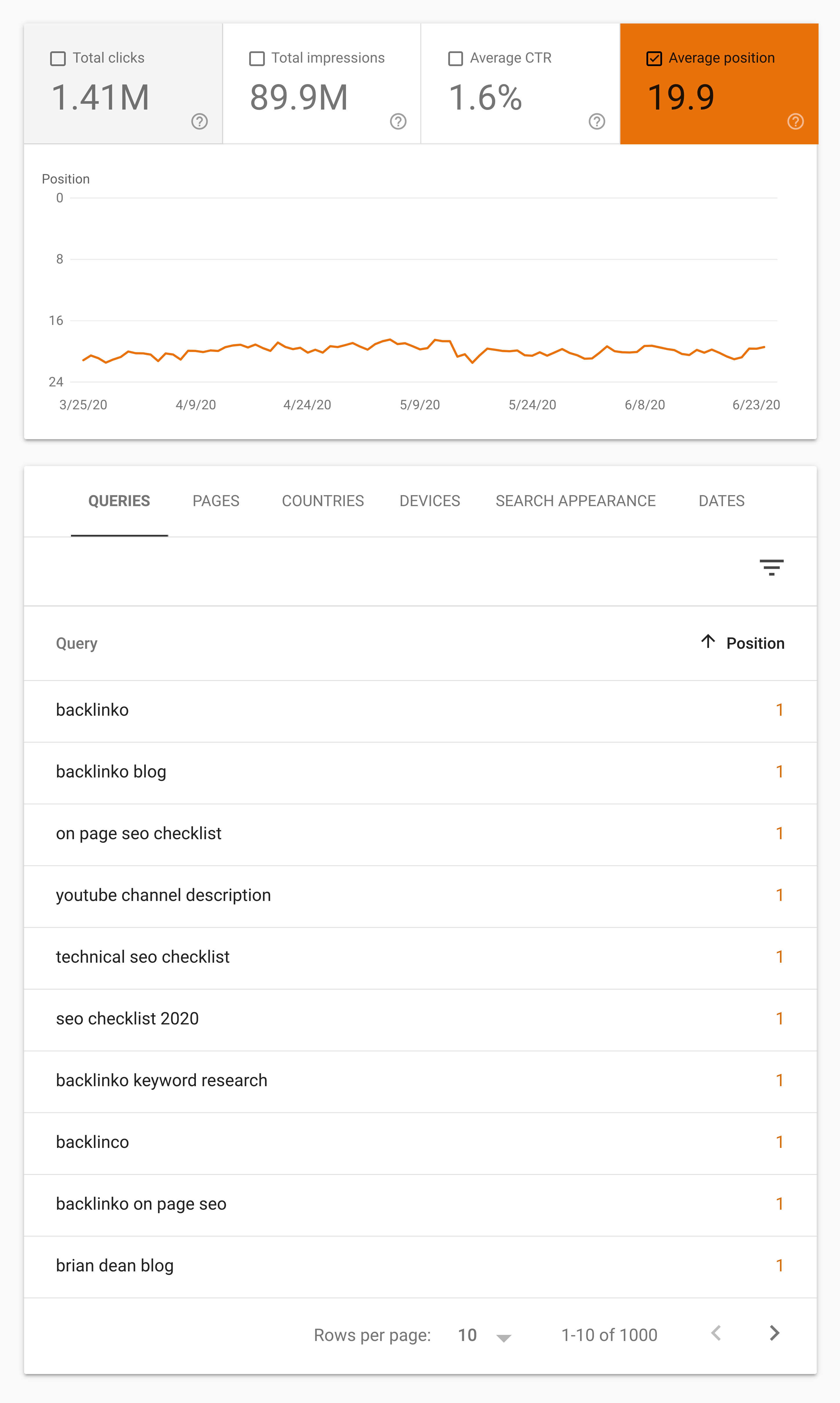
And sort the “Queries” by position. Then, scroll down until you see keywords that have an average position of about 8.

You want to work on those pages first.
(If you’re not sure which pages on your site rank for those keywords, click on the keyword. Then, hit the “pages” tab).

Now that you’ve found the right pages to work on, what’s next?
It depends a lot on the page. If you think that it’s not keyword-optimized super well, then you probably want to focus on on-page optimization.
Or maybe your content is a little outdated. Then you want to make that content up-to-date.
Or let’s say that your content’s UX isn’t that great. Well, you could improve your pagespeed. And use subheadings and large fonts to make your content easier to read and skim.
Rinse and repeat this process for every page that you want to improve.
Step #2: Use Internal Linking
Now that your page is significantly better, it’s time to create internal links that point to that page.
Specifically, you want to add internal links on authority pages on your site. And have those links point to pages that need a rankings bump.
You probably already know the pages on your site with the most link authority.
If not, you can use an SEO tool like Semrush to ID your high-authority pages.
The only other thing to keep in mind here is that you want to use keyword-rich anchor text in your internal links.
That’s because the anchor text you use helps Google understand that your page is “about” your target keyword.

For example, I made sure to make the anchor text for this internal link “on-page SEO”. Which is my target keyword for that page.

Step #3: Optimize for Organic Click Through Rate
Google uses organic click through rate (CTR) to figure out which results are super relevant. And which aren’t a good fit for that keyword.
(I should point out that not every SEO expert agrees with this idea)
For example:
According to the Google Search Console, this page on my site ranks #8 in Google. And it has a CTR of about 3%.
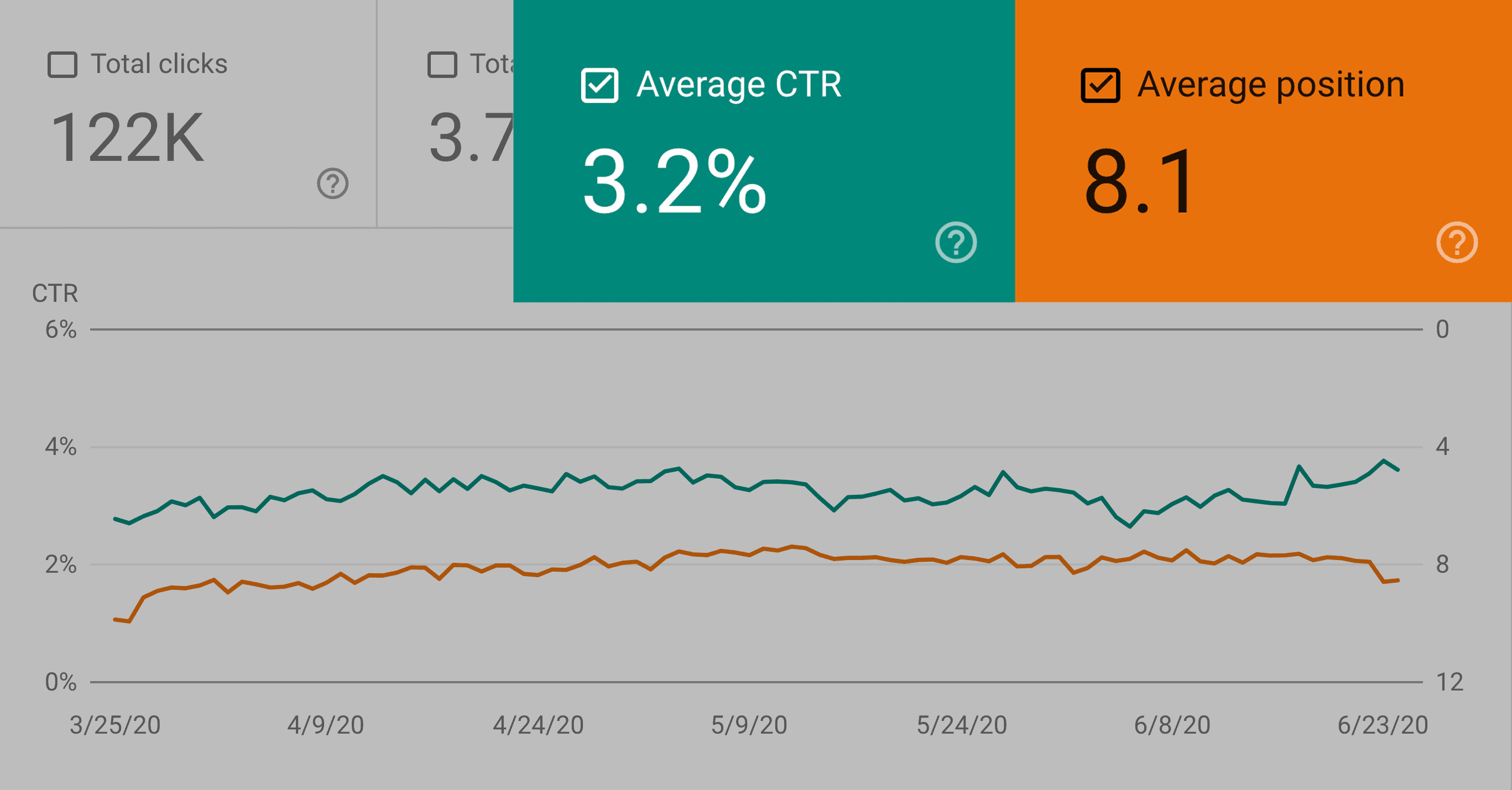
And if I was able to get this CTR to 5% or even 7%, that would send a strong signal to Google that people REALLY want to check out my site. And they’d likely bump me up a few spots.
But if my CTR dropped to 1%, that would send the opposite message. It would tell Google: “People don’t want to see this site in the results for this keyword”. So they’d probably relate me to page 2 or 3.
This video will walk you through some of the things that you can do to get a higher CTR in Google.
Step #4: Improve Your Core Web Vitals Score
Core Web Vitals is a report in Search Console that tells you “how your pages perform based on real world usage data”.
In other words: Google uses Chrome data to see how people interact with your site. And they share that data with you.

Core Web Vitals isn’t a direct ranking signal… yet.
Even so, it’s totally worth optimizing for.
Why?
Well, a bad user experience can directly and indirectly impact your search engine positioning.
For example, let’s say that your page loads slowly. And your content is hard to read.
Well, what are Google users going to do when they land on your page? Hit their “back” button as fast as they can.
Which is going to dramatically increase your bounce rate. And hurt your page’s overall dwell time.
According to a ranking factors study we did, sites with low dwell times tended to rank lower in Google’s results.
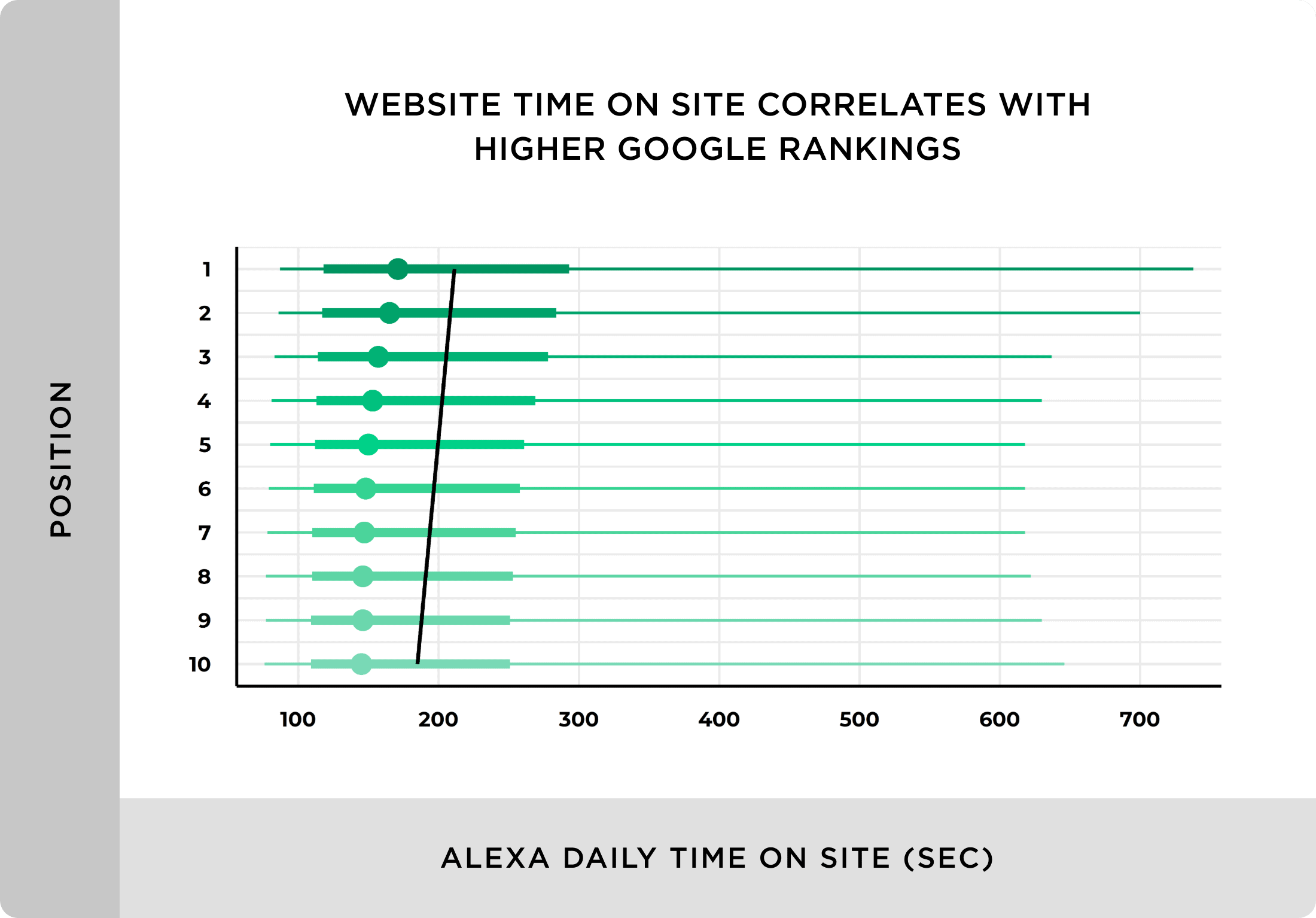
But that’s only the tip of the iceberg. A bad user experience can indirectly hurt your SEO too.
For example, let’s say that a blogger lands on your page. Your content is amazing. AND your Core Web Vitals are on point.
Well, there’s a good chance that the blogger will link to you in a future post. But if your site’s UX was horrible? That same blogger probably wouldn’t stick around long enough to read your stuff.
So yeah, I recommend checking out your Core Web Vitals scores on a regular basis. And improving them as much as you can.
Step #5: Get Multiple Results for the Same Keyword
This is definitely an advanced SEO strategy. So if you’re brand new to SEO, I’d focus more on steps #1-4 here.
That said:
Ranking in multiple spots is a great way to improve your site’s positioning in the SERPs. So it’s worth doing. Especially for keywords that are super important for your business.
There are two main ways to rank in more than one spot.
First, you can get your site to rank in consecutive spots, like this:

This is (obviously) great when it happens.
But it’s hard to specifically optimize for.
The only thing that I’ve seen help is having two pages that cover similar topics. And interlinking between those two pages.
For example, these two pages on my site cover similar topics.

And they both link to one another. Which helps Google see these pages as closely tied together.
But like I said, this doesn’t mean that you’ll automatically get both pages to rank. It’s very hit or miss.
That said, I still think it’s worth doing. After all, ranking twice essentially doubles your search engine positioning for that keyword. Which is pretty sweet.
But there’s another way to take up more SERP real estate: rank content from different websites for the same keyword.
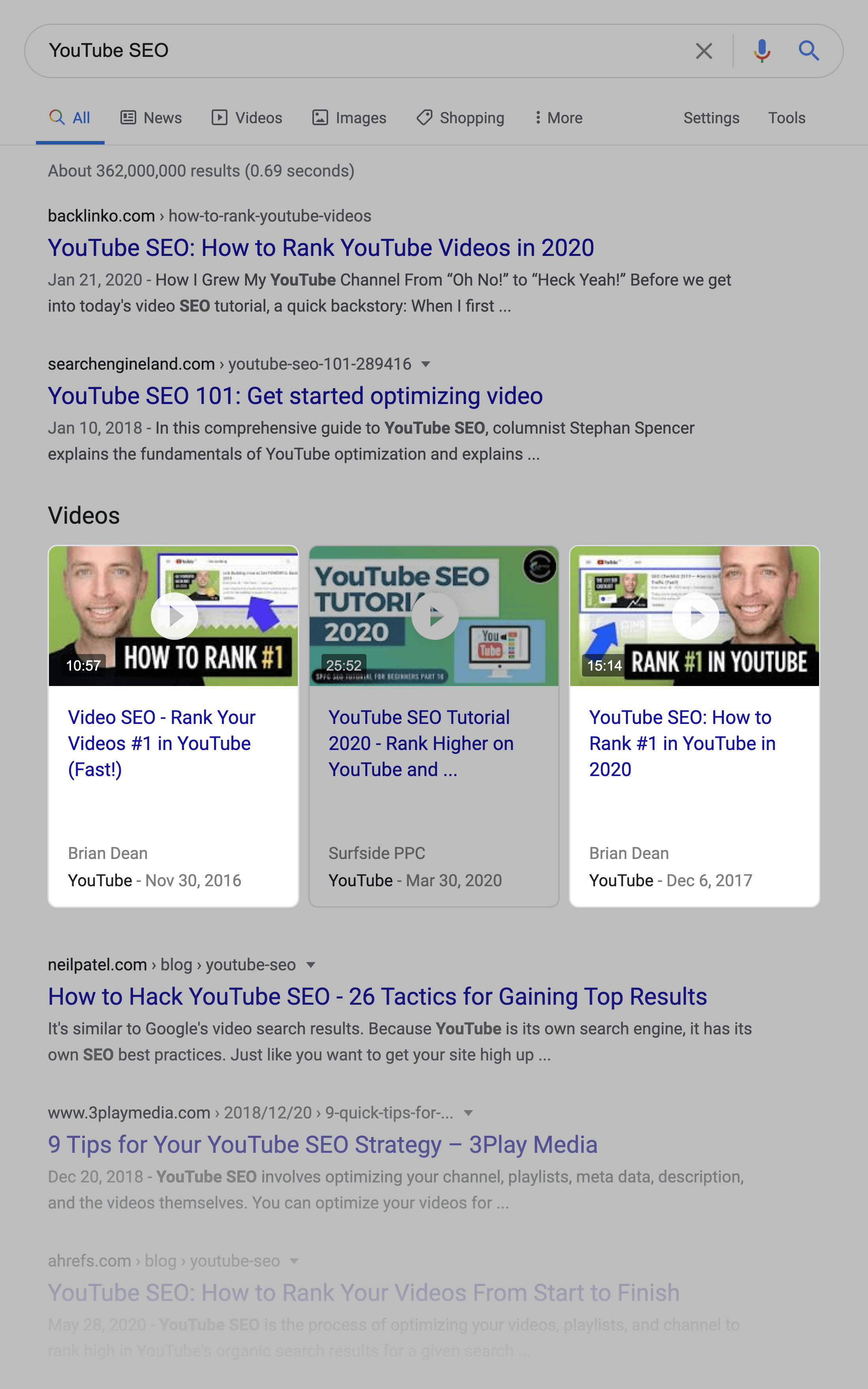
For example, I was able to get my site to rank in the top 3 for “YouTube SEO”.
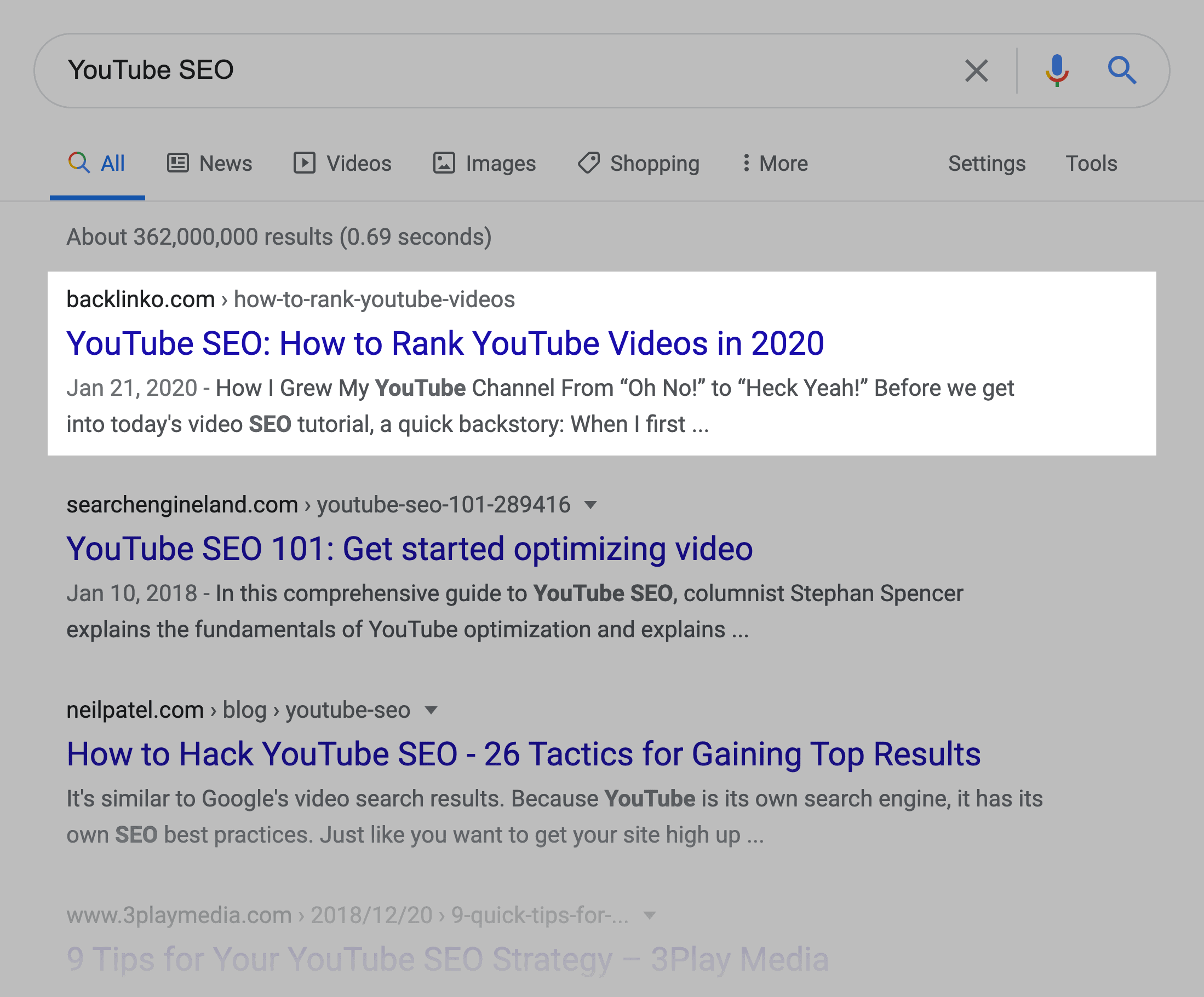
I also created two videos optimized around the same keyword. Those two videos also rank on the first page of Google for that term.
Learn More
How to Create an Effective SEO Strategy: Improving search engine positioning for a specific page is only one part of SEO (although it IS an important one). This in-depth guide shows you how to execute an entire SEO plan from scratch.
The Definitive Guide to Link Building: Thorough guide to building the types of backlinks that Google wants to see.
How to Rank #1 in Google [New Step-by-Step Case Study]: Video that illustrates a lot of the strategies that I outlined here. It also covers topics (like content marketing) that are super important for SEO.